Calculation methods in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Calculator
Calculation methods in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Calculator

Overview of Calculation methods in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Calculator
The Calculation methods in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Calculator is a basic idea in global financial matters, assisting with evaluating the overall worth of various monetary standards and the typical cost for most everyday items across nations. The fundamental hypothesis of PPP depends on the “Law of One Cost,” which recommends that in a productive market, indistinguishable labor and products ought to have similar cost when communicated in a typical money, when the impacts of trade rates are considered. PPP mini-computers intend to gauge this idea and deal a strategy at contrasting costs between various nations. The estimation techniques in PPP adding machines fluctuate contingent upon the particular objectives of the examination — whether it’s contrasting individual merchandise, total files, or changing Gross domestic product information for expansion.
Basic Calculation methods
The essential way to deal with working out PPP is direct on a basic level however can become complicated by and by. The recipe for PPP between two nations is:=Cost of Crate of Merchandise in Homegrown Country/Cost of Crate of Merchandise in Outside Country PPP=Cost of Crate of Merchandise in Outside Country/Cost of Crate of Merchandise in Homegrown Country. This computation considers the correlation of the expense of a comparable crate of products in two nations, adapting to conversion scale contrasts. That’s what the idea is, in a perfect world, the conversion standard between two monetary forms ought to be to such an extent that similar crate of products costs similar in the two nations when evaluated in a typical cash.
Step by Step Calculation methods
1. Characterize the Container of Labor and products
The most vital phase in any PPP estimation is to characterize the crate of labor and products to be utilized for correlation. This bushel regularly comprises of a delegate choice of things that reflect normal utilization designs in every country. The bushel incorporates both tradable products (e.g., food, attire, hardware) and non-tradable merchandise (e.g., lease, medical services, training).
Tradable products:
Things that are normally sent out and imported, like food, vehicles, and hardware.
Non-tradable merchandise:
Things that are by and large consumed locally and are not effortlessly moved across borders, like land and individual administrations (e.g., hair styles, medical care). The choice of the bushel is urgent on the grounds that it impacts the exactness and relevance of the PPP estimation. In a perfect world, the bushel ought to be illustrative of normal utilization designs in every nation, however this can be hard to normalize because of social and monetary contrasts between countries.
2. Measure the Costs of the Crate in Every Country
When the crate of products is characterized, the subsequent stage is to gather cost information for every thing in the bin from the chose nations. Costs are commonly accumulated from significant urban communities or agent areas in every country, with cautious consideration addressed to testing the metropolitan provincial cost differential. The objective is to catch the expense of the bin of merchandise in every country, which will later be analyzed. The value information ought to reflect nearby costs, including variables, for example,
Charges: Deals duty or Tank applied to products.
Endowments: Taxpayer supported initiatives that decrease the expense of specific products (e.g., fuel appropriations).
Import obligations: Duties on imported merchandise that can influence the last cost of items in a given market.
3. Convert Costs Utilizing the Ongoing Conversion standard
Subsequent to gathering the cost information for the bushel of products in nearby monetary standards, the following stage is to change over these costs into a typical money for correlation. This is finished utilizing the ongoing business sector conversion standard between the two monetary forms being referred to. For instance, in the event that we are contrasting the expense of a bin of merchandise in the US (USD) and Japan (JPY), we would take the costs of the products in USD and JPY and afterward convert the cost of products in Japan into US dollars utilizing the ongoing swapping scale among USD and JPY. The equation for the change would seem to be this:
Cost in USD = Cost in JPY × Swapping scale (USD/JPY)
Cost in USD=Price in JPY×Exchange Rate (USD/JPY)
The swapping scale addresses how much the unfamiliar money expected to buy one unit of the homegrown cash (for this situation, the US dollar). It is essential to take note of that trade rates can vary everyday because of changes in economic situations, theory, and international variables.
4. Compute the PPP Swapping scale
When the costs of the bin of merchandise have been changed over completely to a typical cash, the subsequent stage is to compute the PPP swapping scale. This rate mirrors how much unfamiliar cash expected to buy similar container of merchandise in the subsequent nation as would be required in the primary country. The PPP conversion standard between two nations is basically the proportion of the cost of the bin of products in the two monetary forms. The equation for PPP conversion scale between two nations, An and B, can be communicated as:
=Cost of Container in Nation A/Cost of Container in Nation B
PPP=Cost of Container in Nation B/Cost of Bin in Nation A
In this situation:
Cost of Bin in Country An is the expense of similar bushel of merchandise in the main nation (e.g., US).
Cost of Crate in Country B is the expense of similar bin of products in the subsequent nation (e.g., Japan).
The PPP conversion scale shows the number of units of country that B’s cash are expected to buy the very merchandise that can be purchased for one unit of nation A’s money.

5. Adapt to Neighborhood Value Contrasts and Expansion
Subsequent to working out the PPP conversion standard. The following test is to represent nearby cost contrasts (like local value varieties) and expansion rates. These elements can influence the expense of similar container of merchandise. To differ inside a solitary nation or over the long run. To adapt to expansion, PPP number crunchers frequently use expansion changed costs or cost records. For example, the Customer Value List, or CPI) to guarantee that the examination is made between costs that mirror a similar buying control after some time. At times, genuine Gross domestic product or genuine pay correlations. Are made utilizing the PPP conversion scale to adapt to cost level contrasts across nations. This change permits business analysts to look at the general worth of financial result.
6. Utilization of Total Files
While individual PPP examinations between two nations are valuable. PPP mini-computers frequently depend on total records to sum up cost level contrasts across countless nations. For example, the World Bank and the Global Financial Asset (IMF) utilize a total cost record. That covers an expansive arrangement of labor and products, in light of a delegate worldwide bushel. These files are valuable for looking at in general buying power and making cross country monetary correlations.
7. Deciphering the PPP Result
The last step is deciphering the PPP bring about setting. A PPP-based swapping scale assists us with understanding how much money should be traded to keep up with buying influence equality. In the event that the swapping scale between two monetary forms contrasts essentially from the PPP conversion standard, this demonstrates an expected overvaluation or undervaluation of one cash comparative with the other.
For example:
Assuming the market conversion scale is higher than the PPP rate: It recommends that the money in the country with the higher conversion scale might be exaggerated, implying that it takes a greater amount of that cash to purchase similar container of products in the far off country than would be normal in view of relative cost levels. Assuming the market conversion scale is lower than the PPP rate: It recommends that the money might be underestimated, meaning it can purchase more in the far off country than would be normal in view of the cost examination.
Pragmatic Model:
We should expect you need to look at the expense of a container of merchandise between the US and Japan: You characterize a bin of products and gather the costs in the two nations.
Crate in the U.S.: $100
Bin in Japan: ¥12,000
Convert the cost of the bin in Japan into U.S. dollars utilizing the ongoing swapping scale of 1 USD = 110 JPY.
Cost of Crate in Japan in USD: ¥12,000 ÷ 110 = $109.09
Compute the PPP swapping scale:
PPP swapping scale = $100 (U.S. cost) ÷ $109.09 (Japan cost) = 0.916
This outcome suggests that as per PPP, 1 U.S. dollar ought to be worth 0.916 yen to keep up with buying power equality between the two nations. On the off chance that the market swapping scale is altogether unique, it could propose an exaggerated or underestimated money in one or the other country.
Utilization of Value Files in PPP Calculation methods
By and by, most PPP adding machines use value records to gauge the average cost for most everyday items and expansion across nations. The most widely recognized value files are:
Buyer Value List (CPI): This actions the typical change after some time in the costs paid by shoppers for a market crate of labor and products.
Gross domestic product Deflator: A proportion of the value level of all locally created labor and products in an economy.
Maker Value File (PPI): Used to quantify changes in the costs of labor and products sold by makers in a country.
Every one of these files can be utilized in PPP computations relying upon the extension and focal point of the correlation. While CPI is ordinarily utilized for looking at the cost for most everyday items, the Gross domestic product deflator is in many cases utilized while adapting to expansion in Gross domestic product correlations.
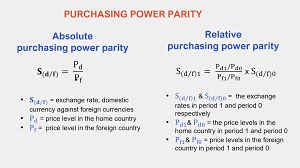
3. Relative versus Outright PPP Estimation
There are two essential types of PPP — outright PPP and relative PPP — and each includes different estimation techniques:
Outright PPP centers around the possibility that the conversion scale between two monetary forms ought to mirror the proportion of costs of a bushel of merchandise between the two nations. It accepts that no transportation expenses or exchange obstructions exist, and merchandise are entirely indistinguishable in all nations. The computation strategy for outright PPP is basically an immediate examination of costs between two nations, changed by the swapping scale. Relative PPP depends on the hypothesis that adjustments of trade rates after some time are corresponding to changes in the cost levels between two nations. This is the most ordinarily involved type of PPP in genuine applications, as it represents expansion rates and is utilized to foresee future conversion scale developments.
4. Changes at Neighborhood Varieties in Costs
One of the difficulties in PPP estimations is representing the way that costs can shift broadly in any event, for similar merchandise across various districts of a country. For example, a portion of bread might cost more in a metropolitan region contrasted with a provincial region. PPP number crunchers should adapt to these provincial value contrasts to give a more precise correlation of buying power. This should be possible through inspecting procedures, where costs are gathered from various areas inside every country.
5. The Job of the Crate of Products in the Calculation methods
In PPP computations, the determination of the crate of labor and products is vital. A normal bin could incorporate food, dress, transportation, and lodging. Yet the specific creation can change in view of the nation or the particular objectives of the correlation. For instance, in richer countries, the bin may be acclimated to incorporate all the more top of the line labor and products. While in emerging nations, the spotlight might be more on essential necessities. The bushel of products utilized in the estimation can likewise be dynamic. Changing over the long run to reflect advancing utilization designs.
6. Adapting to Non-Tradable Products in Calculation methods
One restriction of PPP is its emphasis on tradable merchandise. Non-tradable products, similar to land and individual administrations (e.g., hair styles). Can display huge cost contrasts that are hard to adapt to. For instance, land costs in New York City might be decisively higher than in provincial China. In any event, while nearby buying power is thought of. Some PPP adding machines endeavor to represent these distinctions by consolidating assessed costs for non-exchanged products. However the precision of these changes can shift.
7. Information Sources and Conglomeration
Precise PPP computations rely upon admittance to solid information. Significant establishments like the World Bank and the Global Money related Asset (IMF) routinely gather information from nations all over the planet. Which is utilized in their PPP-based reports and correlations. This information can be collected at various levels, from individual urban communities to whole nations. To give a worldwide perspective on buying power. The total cycle includes averaging the costs for a particular bushel of merchandise across various locales or nations. Which is then adapted to conversion standard contrasts.
8. Restrictions and Reactions of Calculation methods
While PPP is an integral asset for contrasting the cost for most everyday items. And financial movement across nations, there are a few limits to its utilization. As referenced, PPP estimations are best for contrasting tradable merchandise. And can be slanted by non-tradable products, provincial value varieties, and contrasts in utilization designs. Moreover, the information assortment cycle can be troublesome in low-pay or less-created nations. Where the value information might be less exact. Another analysis is the presumption that all labor and products are indistinguishable in each country. Which neglects nearby inclinations, quality contrasts, and different elements that can influence the cost and attractiveness of merchandise. Also, PPP doesn’t represent contrasts in government approaches. For example, charges or appropriations, that can falsely adjust the average cost for most everyday items.

Other Calculation methods in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Calculator
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is an idea used to look at the general worth of monetary standards between various nations. It expects to decide the swapping scale that would adjust the buying force of two monetary standards by thinking about the costs of labor and products.
1. The Relative Strategy:
One normal technique for ascertaining PPP is the relative strategy. This approach looks at the value levels of a bin of labor and products in various nations. By looking at the costs of indistinguishable or comparative merchandise, financial specialists can gauge the general buying force of various monetary forms.
2. The Worldwide Correlation Program (ICP):
The ICP is a worldwide factual drive that gathers information on costs and consumptions across nations. It gives a far reaching structure to working out PPP by gathering information on a large number of labor and products. The ICP utilizes studies and factual procedures to guarantee exactness and equivalence of information.
3. The Large Macintosh Record:
The Enormous Macintosh File is a well known casual technique for assessing PPP. It looks at the costs of a Major Macintosh burger across various nations to decide the overall worth of monetary forms. This file depends on the hypothesis that a Major Macintosh ought to cost a similar in each nation when switched over completely to a typical cash.
4. The Geary-Khamis Strategy:
The Geary-Khamis technique is a more complicated way to deal with working out PPP. It considers the costs of labor and products as well as the distinctions in quality and amount. This technique utilizes an arrangement of conditions to gauge the overall buying force of various monetary standards.
5. Time Series investigation:
One more strategy used to ascertain PPP is time series examination. This approach analyzes the progressions in cost levels over the long run to decide the general buying force of monetary standards. It considers expansion rates and other monetary elements that influence cost levels. It is critical to take note of that these techniques have their constraints and suppositions. They give assesses as opposed to correct qualities, and the precision of the estimations relies upon the quality and accessibility of information. Financial analysts proceed to refine and foster new techniques to work on the precision of PPP estimations.
Development in real life by Calculation methods of PPP Calculator
To mimic information assortment at scale, understudies gathered item data including all credits and costs from online sources. Utilizing a python calculation that put away examples of item information utilizing AWS DynamoDB. When the information were put away. The following period of the arrangement was to extricate significant pieces of the example information that would be valuable for item coordinating. Item portrayals, for example, “All Natural* 73% Lean/27% Fat Lean Ground Hamburger” aren’t tracked down. Under similar headings in information starting with one retailer then onto the next.
The group utilized regular language handling (NLP) by means of profound learning and the Spacy.io Python library to settle this. Given a couple of equivalent words for an item quality, the Spacy calculation extricated the pertinent qualities. Regardless of whether keys were named completely not the same as information source to information source. For instance, it perceived that the item portrayal. Fat Lean Ground Meat was under the ‘title’ key from one internet based information source. Conversely, from another source, it perceived the undertaking title from the ‘name’ key.
Conclusion
All in all, buying power equality (PPP) is a valuable macroeconomic marker. That assists with contrasting the buying force of various monetary standards comparative with the U.S. dollar. It estimates the expense of a container of labor. And products in various nations in the wake of changing their monetary standards to the U.S. dollar. Also, it empowers the correlation of financial markers like GDP (Gross domestic product). Expansion, expectations for everyday comforts, and wages across nations to survey their general monetary exhibition.